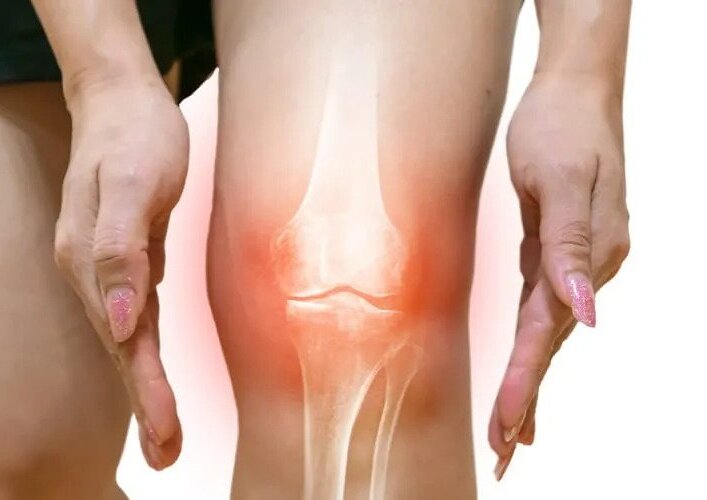
 Knee arthritis is a medical condition that refers to the inflammation of knee joints that leads to various symptoms such as pain in the knee along with stiffness, swelling, tenderness (pain on touching affected area), popping or cracking sounds when one moves the knees, and restricted motion of the knee joint. In chronic cases of arthritis, deformities in the knee joint are observed.
Knee arthritis is a medical condition that refers to the inflammation of knee joints that leads to various symptoms such as pain in the knee along with stiffness, swelling, tenderness (pain on touching affected area), popping or cracking sounds when one moves the knees, and restricted motion of the knee joint. In chronic cases of arthritis, deformities in the knee joint are observed.
Homeopathy has a lot of potential for treating cases of knee arthritis. Homeopathic remedies primarily work in providing relief in its symptoms such as stiffness, pain and swelling of the knee. Simultaneously, it reduces inflammation in the joint and stops further damage to the joint. This stops any further aggravation of the disease. Homeopathic medicines prove effective in both acute and chronic knee arthritis cases. Homeopathic intervention carried out at the right stage can offer highly promising results in knee arthritis cases. In the cases that fall under the mild to moderate category, complete recovery may depend on the cause behind damage. However, in severe cases, symptom management may occur though the degenerative changes that have already occurred and cannot be reversed. In severe cases, these medicines can be administered with allopathic medicines as well, since they do not interact.
How Homeopathy Treats Knee Arthritis?
1. Homeopathy treats the root cause: Homeopathic medicines work wonderfully in cases of knee arthritis. It treats the root cause behind the disease. There are various causes behind knee arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, injury, etc. The homeopathic medicines do not act in a superficial manner but reach the core targeting the root cause and offers wonderful results in such cases instead of suppressing the symptoms.
2. Safe and non-toxic on the body: Homeopathic remedies are safe and natural to use which do not have any side effects. In the conventional mode, medicines such as pain killers, NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti – inflammatory medicines, corticosteroids, and DMARDs (disease modifying anti rheumatic drugs) are prescribed for knee arthritis depending on the cause. These medicines provide temporary relief, can be habit forming and also bear various kinds of side effects. The homeopathic system of medicines has an edge over conventional treatment as it provides relief that is not short-lived and has a lasting effect and it does not create any dependence.
3. Individualized approach to treatment: Homeopathic remedies are administered individually for every case after thorough detailed case based in-depth evaluation of symptoms. Therefore, it is advised to take homeopathic medicine for knee arthritis only after consulting a qualified homeopath. Self-medication should be strictly avoided since the prescription, potency, dosage and repetition varies from case to case basis.
Top 11 Homeopathic Medicines for Knee Arthritis
The most important homeopathic medicines to treat knee arthritis are Rhus Toxicodendron, Bryonia Alba, Apis Mellifica, Benzoicum Acidum, Osteo-Arthritic Nosode, Arnica Montana, Ledum Palustre, Calcarea Carbonica, Pulsatilla Nigricans, Causticum and Ruta Graveolens.
1. Rhus Toxicodendron – Top-Grade Medicine for Knee Arthritis
Rhus Toxicodendron is administered as the first line of treatment for managing most of the cases of knee arthritis. The foremost indication for its use is pain in the knees even at rest. Even a few steps of walk offers relief and as one continues to walk, more relief sets in. The pain is tearing along with marked stiffness. The knee can be swollen as well. This medicine helps in relieving stiffness, pain, swelling of the knee and improves its range of movement.
When to use Rhus Toxicodendron?
Rhus Toxicodendron can be administered when knee pain aggravates during rest. As one starts walking, relief starts to set in not just from pain but also from knee stiffness.
How to use Rhus Toxicodendron?
It can be administered in both low and high potencies, but it is usually recommended in 30C power twice to thrice daily as per the severity of the symptoms.
2. Bryonia Alba – For Knee Pain Getting Worse on Movement
It is the second most valuable medicine for knee arthritis sourced from the roots of plant ‘Wild Hops’. It is the most frequently administered medicine for those who experience knee pain with every little movement and only complete rest provides comfort. Most of the times, they bear stitching types of pain while walking. The knee may be swollen and red. Marked stiffness in the joints along with pain is also a characteristic feature to administer this medicine.
When to use Bryonia Alba?
This medicine is the best solution for the knee pain which restricts the patient from all kinds of movements (as the slightest knee movement causes pain) while rest eases the pain.
How to use Bryonia Alba?
Bryonia Alba can be administered in 30C power two to three times a day for best possible results. Potency can be enhanced to 200C or 1M after consulting a qualified homoeopath.
3. Apis Mellifica – For Arthritis with Swollen and Painful Knees
This medicine is of great use in the cases of knee arthritis where pain in the knee is accompanied by marked swelling. The knee is shiny, sensitive, red and sore to touch. The nature of pain most of the time is of shooting/stinging in nature. A large burning sensation is felt in the knee. Individuals who need this medicine have marked intolerance to heat and all their complaints aggravate even from slightest touch.
When to use Apis Mellifica?
This medicine can be administered when the knee is inflamed and extremely painful with noticeably felt stinging pain.
How to use Apis Mellifica?
To start with, one can administer Apis Mellifica 30C two to three times daily. Gradually the dose can be reduced when the symptoms improve.
4. Benzoicum Acidum – For Knee Arthritis Due to High Uric Acid Levels (Gout)
Benzoicum Acidum is the best prescription to manage knee arthritis and pain that results from high uric acid levels (gout). Those who need it complain of swelling and pain in the knee. Along with this, cracking sound emanates when the knees moves, and dryness can be felt inside the knee. Crackling sound from knees on movement may also accompany the pain.
When to use Benzoicum Acidum?
This medicine is administered as the first remedy in case of pain, knee inflammation, and swelling due to high uric acid levels.
How to use Benzoicum Acidum?
It usually works wonders in low potencies. Usually it is recommended in 30C potency twice to thrice daily for best possible results.
5. Osteo-Arthritic-Nosode – For Osteoarthritis of Knee
Osteo-Arthritic-Nosode (OAN) is a homeopathic medicine prepared from the synovial fluid of an osteoarthritic knee. This medicine is a specific medicine to treat cases of osteoarthritis of knee. This medicine is known to relieve pain (especially at night) and stiffness in the joint (especially in the morning). It reduces knee swelling and also helps improve the range of joint movement.
When to use Osteo-Arthritic-Nosode?
This medicine is mainly used as an intercurrent remedy (in cases where improvement has come to a standstill to help to remove any factors that are blocking further improvement) in knee osteoarthritis cases. It helps relieve one of stiffness and joint pain at night and in the morning.
How to use Osteo-Arthritic-Nosode?
It is mostly administered in 200C potency on a weekly basis (means one dose per week only). Do not exceed the dose.
6. Arnica Montana – For Arthritis Developing Post Injury
This medicine is one of the top medicines that helps manage arthritis that may arise from an injury. It is highly effective to reduce swelling in the knee and pain which is a sore and bruised type. Along with pain management, Arnica heals the injured areas of knee joint and reduces joint inflammation, and halts the worsening of symptoms. Sore, bruised feeling in the joints is the characteristic symptom to administer this medicine.
When to use Arnica Montana?
This medicine can be administered in cases presenting with post-injury knee arthritis with bruised and sore type pain and swelling in the knees.
How to use Arnica Montana?
It can be administered in 30C potency twice to thrice daily depending on the severity of pain.
7. Ledum Palustre – For Arthritis with Knee Cracking Sounds
Ledum Pal is a very effective medicine for managing knee pain accompanied by cracking sound when one moves the knee. The pain in knee aggravates from movement. Along with this, there is stiffness, swelling, and weakness in the knees. One of the main symptoms to administer this medicine is the ascending type of rheumatism, i.e., rheumatic pains begin in lower limbs and move upwards.
When to use Ledum Pal?
This medicine is administered to manage cases of knee pain with cracking sound when the knee is moved.
How to use Ledum Pal?
This medicine can be administered twice a day in 30C power. Its higher potencies can also be used afterwards under guidance of a homeopathic physician.
8. Calcarea Carbonica – For Knee Arthritis Linked to Obesity
Calcarea Carbonica is a deep constitutional remedy affecting bones, joints, and metabolism. Key signs for its use are knee pain due to a patient being overweight, flabbiness along with weakness of knee joints and if one gets fatigued easily. Pain worsens from exertion, climbing stairs and in cold weather. There is marked stiffness after rest. Arthritis associated with early degenerative changes is wonderfully treated with this medicine.
When to use Calcarea Carbonica?
This medicine should be administered in cases of arthritis with weak bones and joints associated with obesity, easy exhaustion and early to mid-stage degenerative knee arthritis. Osteoarthritis is usually associated with poor metabolism and weight gain. Patients report slow recovery and there are recurrent complaints.
How to Use Calcarea Carbonica?
It can be used in 30C power for acute episodes. The potency can be enhanced to 200 and 1M depending on the intensity of the symptoms. Avoid frequent repetition once improvement sets in.
9. Pulsatilla Nigricans – For Arthritis with Changeable Joint Pains
Pulsatilla suits mild, yielding individuals with changeable symptoms. This medicine is effectively used in cases of arthritis with knee pain constantly changing location and even severity. Pain noticeably aggravates in warm rooms and it gets better in open air. Stiffness may also accompany that gets worse towards the evening. Arthritis among women, especially with hormonal imbalance and associated with emotional sensitivity is well managed by administering this medicine.
When to use Pulsatilla Nigricans?
Pulsatilla is typically used in cases of arthritis where knee pain changes location. It gets better in open air and worsens when there is warmth.
How to use Pulsatilla Nigricans?
It can be administered in 30C potency one to two times daily. It can be administered safely for longer durations with monitored doses under guidance of a qualified homoeopath.
10. Causticum – For Chronic Stiffness and Deformities in Joints
Causticum is administered in chronic rheumatic and paralytic cases. It is effectively used in chronic arthritis cases with progressive stiffness. Weakness and instability of knees is another key symptom to use Causticum. Pain typically gets worse in cold and dry wind. Patients who require this medicine have difficulty in rising from a sitting position. Its use is also recommended in early joint deformity and contractures.
When to use Causticum?
Causticum proves to be efficacious in cases of arthritis with chronic stiffness, weakness and deformity of the knee joint. It is administered in chronic knee arthritis cases or if the disease progressed significantly, especially among elderly patients with who face difficulty initiating movement.
How to use Causticum?
It can be used in 30C potency for acute episodes of pain. The potency can be enhanced to 200 and 1M depending on the severity of the symptoms. Gradually reduce the doses once improvement begins.
11. Ruta Graveolens – For Knee Arthritis Due to Repeated Exertion and Overstraining
Ruta Graveolens has a special affinity for periosteum, tendons, and ligaments. It wonderfully treats cases of arthritis if there is knee pain due to overuse, strain, or repeated exertion. Pain aggravates while climbing stairs or kneeling with marked lameness and stiffness in the knee joints. Sensation of bruised soreness may also accompany. This medicine is most useful when arthritic changes involve tendons around the knee.
When to use Ruta Graveolens?
Ruta Graveolens is the best choice of medicine in case of arthritis if there is soreness or lameness of joints due to overstraining and exertion. It also helps treat post-traumatic or occupational knee stress.
How to use Ruta Graveolens?
It can be used in 30C potency one to or two times daily for best possible results.
Note: Do not exceed the use of any of these medicines in more than the recommended potency and dose. You may continue these medicines for about a month. To use beyond that or to use high potencies, strictly consult a qualified homeopath.
Causes of Knee Arthritis and Its Symptoms
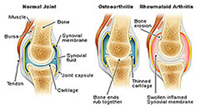
Before learning the causes of knee arthritis, let us first review the structure of knee joints. The knee is the strongest and the most complex joint in the body. It is responsible for bearing body weight and movement. It is made of bones, meniscus, muscles, ligaments and tendons. The bones that can get affected in knee arthritis include lower end of thigh bone (femur), upper end of a bone in leg called tibia and knee cap called patella in front of knee. Between thigh bone and tibia, two meniscuses are present. Meniscus is C-shaped tough, rubbery cartilages that work as a shock absorber and stabilize the joint and prevent direct rubbing of bones against each other. The knee joint is surrounded by a synovial membrane that releases fluid to keep the joint lubricated and reduces friction on movement. Small fluid-filled sacs called bursa are present in the knee joint that function to decrease friction between knee tissues during movement. Any of these components of the knee can be affected in case of knee arthritis.
Knee arthritis can happen due to several reasons but the majority of the causes are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis and injury (post traumatic arthritis).
1. Osteoarthritis
One of the most common causes of knee arthritis is osteoarthritis of the knee joint. From among over 100 different types of arthritic conditions, osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. This is most common in old and middle age. Osteoarthritis generally affects the weight-bearing joints such as the knee, but it may harm any other joint too.
What is the Cause and how does it affect the knee joint?
The real cause of osteoarthritis is not very clear. Medical researchers believe that it is due to a combination of factors that include injury to the joint or stress, aging, being overweight and genetic factors.
Osteoarthritis affects the knee joint by destroying the cartilage in the knee joint which slowly degenerates. Cartilage is made up of a protein substance that acts as a cushion between the bones of the joints. In advanced cases of osteoarthritis, the cartilage may disappear and the bones start rubbing against each other causing more pain. When bones start rubbing against each other, bony growth may occur around the joints.
Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis
In the initial stages of knee osteoarthritis, one may simply feel severe pain in the knee joint. As the problem advances, common symptoms include the pain that aggravates after an exercise session or weight bearing, swelling in the joint, limited movement of the knee joint, stiffness during periods of inactivity such as sleeping or sitting; cracking or grating sounds in the knee joint. As the damage to the knee joint worsens, the joint may become less movable and pain may occur even when the joint is at rest. The symptoms may keep the patient awake throughout the night.
Stages of Knee Osteoarthritis
Stage 1: Early and mild stage, there is very minimum wear and tear of the cartilage and no significant narrowing of the joint spaces.
Stage 2: Moderate Arthritis, symptoms occur more frequently and the cartilage begins to breakdown causing narrowing of the joint spaces. Osteophytes are seen at this stage.
Stage 3: Severe Arthritis, persistent pain and stiffness is there with severe cartilage loss leading to loss of joint spaces and bones rubbing together. Large osteophytes are also seen.
Stage 4: End stage with severe degeneration of joint and adjoining structures, one struggles to walk and there is total loss of cartilage. Joint deformities such as “bow legs” and “knock knees” are commonly seen at this stage.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
It is an autoimmune disorder that results in stiffness, joint pain, swelling and reduced movement of the joint. An autoimmune disorder means the immune cells start damaging the healthy tissue of the body due to a misdirected response. In most cases, RA starts from small joints but later affects large joints as well, including the knee. It tends to affect the same joint bilaterally (on both sides) at a given time.
Why and how does it occur?
The exact reason for it is not clear. However, it seems to begin from an interaction between genetic susceptibility (persons having HLA – DR1 and HLA – DR4 genes are at high risk of it) and environmental factors (some infection with virus, bacteria and smoking). In RA, inflammation occurs in the synovial lining of the synovial membrane and with progression causes destruction of the cartilage and the bone of the joint.
Signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis affecting knee
1. Swelling and knee pain
2. Knee stiffness gets aggravated in the morning, lasting for an hour, and as one gets active relief starts setting in
3. Heat and tenderness in knee joint
3. Gout (Hyperuricemia)
What is gout and why does it occur?
Gout means inflammation of the joint due to high uric acid levels. This type of arthritis arises when uric acid crystals (monosodium urate crystals) collect in the joint. These are needle-like crystals that set off inflammation and swelling in the joint. Though, mostly it affects the big toe joint, it can also occur in other joints, including the knee
Symptoms when gout attacks the knee
1. Knee pain
2. Knee swelling
3. Redness, warmth and tenderness on knee
4. Injuries (Post-Traumatic Arthritis)
Injury to the knee joint can also trigger arthritis referred to as post-traumatic arthritis, that can result in osteoarthritis. It may begin after an injury to ligament, meniscus tear or broken bone. The wear and tear makes the knee joint unstable and puts extra pressure on the joint that may develop into arthritis subsequently.
Diagnosis of Knee Arthritis
The diagnosis of knee arthritis involves clinical evaluation, medical history and few imaging and blood tests.
1. X-ray of the affected knee — This is the first test administered to diagnose a case of knee arthritis. This test helps to find bone spurs, narrowing of joint space and other bone changes.
2. Blood tests — ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) and CRP (C-reactive protein) are advised to get an idea of the severity of the inflammation.
3. Rheumatoid factor qualitative and Anti CCp (anti – citrullinated protein antibody) — In cases suspected of rheumatoid arthritis.
4. Uric acid levels if symptoms point towards gout.
5. In advanced cases, MRI or CT scan could be needed to get more details of bones and to look into changes in the soft tissue of the joint.
Management and Lifestyle Changes in cases of Knee Arthritis
1. Role of exercise: Regular exercise helps strengthening the muscles around knees and improving joint mobility. Low-impact activities such as cycling, swimming, and walking are best recommended as they put less strain on the knees. Focus should be on strengthening the quadriceps and calf muscles that mainly supports the knee.
2. Weight Management: Obesity and being overweight makes an individual more prone towards developing arthritic conditions of the knee joint. Managing ones weight can help reduce pressure on the knee joint and reduce the inflammation thus leading to gradual relief in symptoms.
3. Dietary Recommendations: Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as omega-3 fatty acids, green vegetables, fresh fruits, and whole grains. Avoid high protein foods in cases of gout or raised uric acid levels. Control your calories to manage weight.
4. Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat to the affected joints (using warm belts or heating pads) can relax the stiff muscles and improve blood flow. Applying cold pack or ice compression on the affected joint helps reduce inflammation and provides relief from pain.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do I feel stiffness in my knees, especially in the morning or after rest?
Stiffness occurs because the joint becomes less lubricated when not in use. Once you start moving, circulation improves and the stiffness gradually reduces.
2. Is knee osteoarthritis only seen among the elderly?
No. Although it is more common with increasing age, knee osteoarthritis can also affect younger individuals due to obesity, excessive strain, earlier injury, or bad posture.
3. Will knee osteoarthritis keep getting worse?
The progression varies from person to person. With proper treatment, weight control, lifestyle changes, and exercises, symptoms can be controlled and progress can be gradual.
4. How long does it take to improve with homoeopath treatment?
Relief may set in within a few weeks, but long-term improvement usually requires regular treatment and follow-ups, as osteoarthritis is a chronic condition.
5. Do I need surgery if I have knee osteoarthritis?
Most patients do not require surgery. Many cases can be effectively managed with medicines, exercises, physiotherapy, and lifestyle changes. Surgery is considered only in advanced cases.
6. Should I completely stop exercising or walking?
No. Complete rest can aggravate stiffness. Gentle exercises and short walks are better, while exertion, squatting, and climbing stairs excessively should be avoided.
7 . Can knee osteoarthritis be cured completely?
Osteoarthritis cannot be reversed, but symptoms can be managed and quality of life can be made better with proper care.
8. Why does my knee pain increase while climbing stairs or getting up from a chair?
These activities put extra load on the knee joint. When the cartilage is worn out, movements like climbing stairs or standing up cause more friction and pain.
9. Why do I hear cracking or grinding sounds from my knees?
Cracking or grinding (crepitus) occurs due to irregular joint surfaces and reduced joint lubrication. It is common among patients suffering from knee osteoarthritis and not always a sign of aggravation of disease.
10. Is swelling normal in knee osteoarthritis?
Yes. Mild to moderate swelling can occur due to joint inflammation or excess fluid formation, especially due to overuse.
11. Does cold or damp weather affect knee pain?
Many patients notice increased stiffness and pain in cold or damp weather because such conditions affect circulation and joint flexibility.
12. Can knee osteoarthritis affect both knees at the same time?
Yes. Knee osteoarthritis mostly affects both knees, though one side could be more painful than the other.
13. Is walking with support (stick or knee cap) helpful?
Yes. Using a knee cap, walking stick, or brace reduces pressure on the knee joint and provides stability, especially among the elderly.
14. Are painkillers the only solution for knee pain?
No. Painkillers give temporary relief. Long-term management includes exercises, weight control, medicines, and lifestyle modifications that are helpful in managing knee arthritis to assure long term relief.
15. Can stress or emotional factors worsen knee pain?
Yes. Stress can enhance muscle tension and pain perception, aggravating knee symptoms.